Python Filters
Python is an interpreted high-level general-purpose programming language.
Installing Python
Before you can run Python filters, you will need to install python.
Please ensure that you add python to your path:
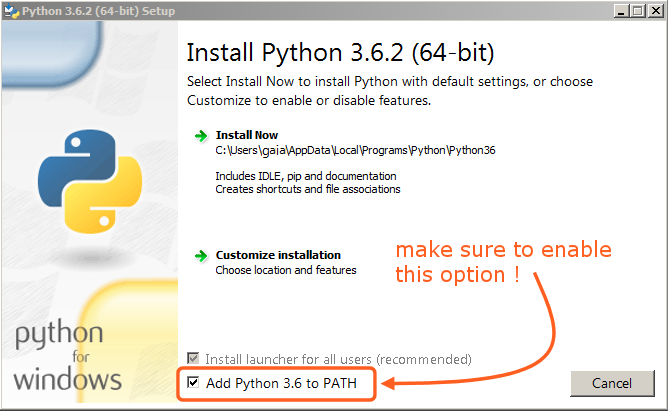
We recommend that you download more or less recent versions of Python.
WARNING
It's generally not acceptable to install python via the Microsoft Store. Python installed from here is not available on the path. If you have trouble running Python filters with Regolith, please reinstall using the link above.
Running Python code as Filter
The syntax for running a python script is this:
json
{
"runWith": "python",
"script": "./filters/example.py",
// Optional property that defines the path to the file with the requirements
"requirements": "./filters/requirements.txt
}
Requirements and Dependencies
When installing, Regolith will check if the filter has any requirements. If the "requirements" property is set, Regolith will use the file specified in the property to install the dependencies. If the property is not set, Regolith will look for a file named "requirements.txt" in the same directory as the script. If requirements file exits, Regolith will attempt to install these dependencies into a venv, as described below.
When developing a Python filter with dependencies, you must create this file. You can create a requirements.txt file yourself by using pip freeze.
Venv Handling
Python Venvs are flexible, lightweight "virtual environments".
Regolith uses venvs to install dependencies, since it will prevent your global installation space from becoming polluted. When you install a python filter with dependencies, they will be installed into a venv, stored in .regolith/cache/venvs/.
By default, all filters will share a single venv.
In case of collision, you may use "venvSlot": <int> property in the filter, to claim a unique venv id. You will need to reinstall the filter.
 Regolith
Regolith